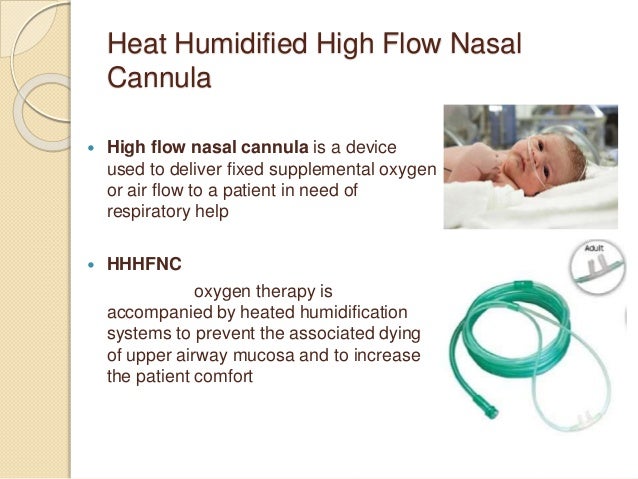
Heat and humidified high flow nasal cannula or as most call it hi flow nasal cannula hfnc isn t just a standard nasal cannula cranked up to very high flow rates.
High flow oxygen devices ppt.
These devices monitor delivered oxygen concentration supplied via a low pressure system in the delivered gas.
2009 6 9 1 11 bailey p thomsen ge spuhler vj et al crit care med jan2007 35 1 139 145.
Delivery devices work with different flow rates.
The humidifier should always be placed at a level below the patient s head.
The flows are such that the patient will not be entraining room air that will lower the fio2.
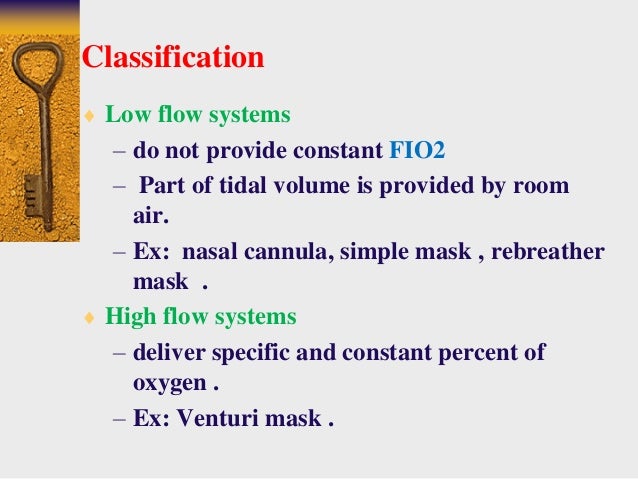
Oxygen therapy can be delivered using a low flow or high flow system.
Oxygen delivery devices dr.
The system provides a high flow of heated humidified air to the patient via the nasal cannula.
Low flow device most common device used for mild hypoxia can be set between 1 and 6 lpm 24 to 40 fio2 fio2 increases approximately 4 with each liter of o2 korupolur gj needham dm contemporary criticalcare.
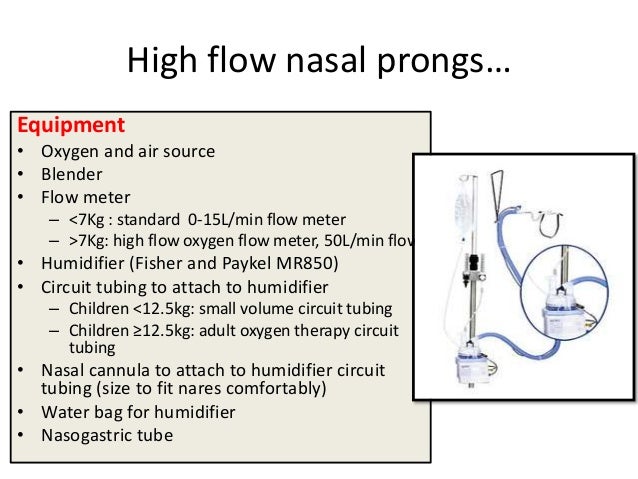
All high flow systems require humidification.
High flow oxygen devices these devices meet the inspiratory flow of the patient and generate accurate fio2s so long as there is a good seal between the mask and the patient s face.
It varies from 0 15l per minute.
High flow can thus be generated even though air and high pressure oxygen wall supplies are unavailable.
Respiratory rate and tidal volume of the patient have no.
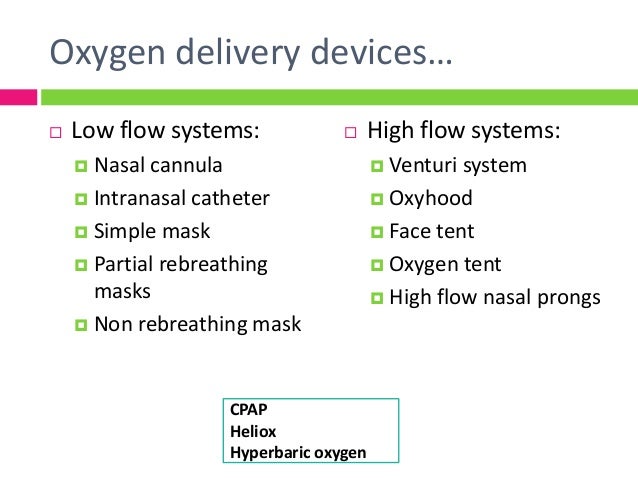
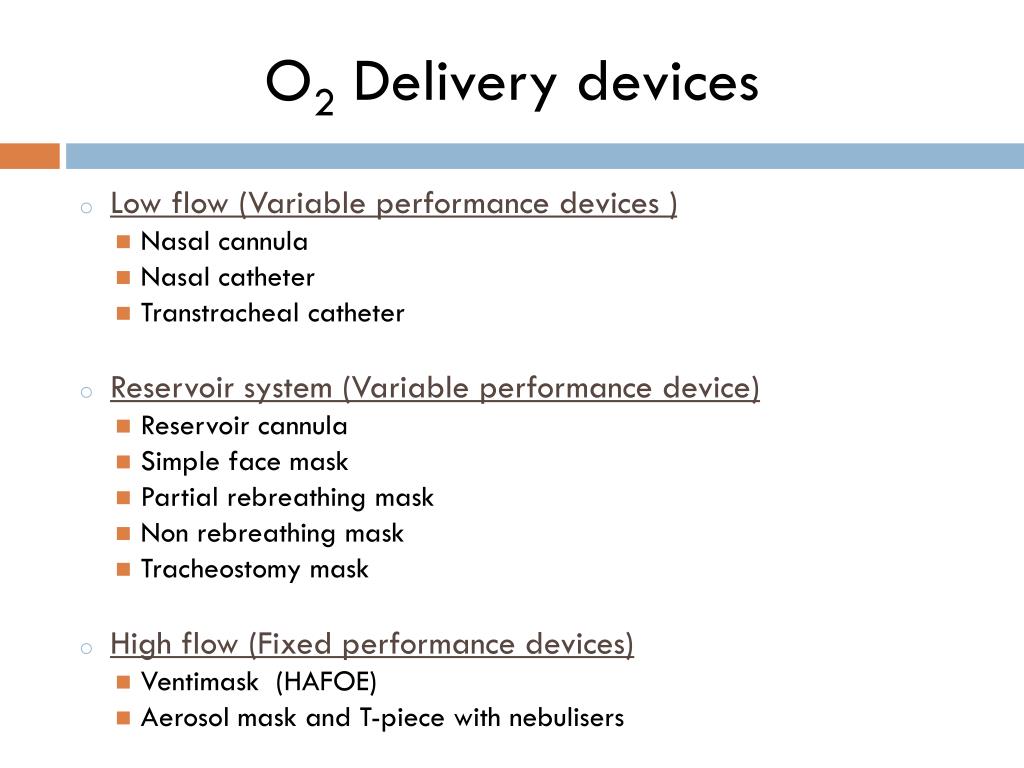
They include nasal cannulae.
The flow rate can be set on the wall tap.
Indications of o2 therapy 1.
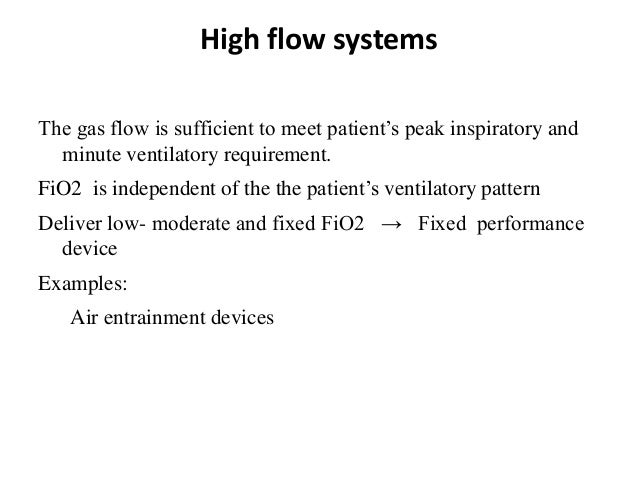
Page high flow gas delivery systems supply all the gas the patient needs.
The percentage of oxygen inspired depends on the flow rate and the delivery device.
In this video george gives a short review differentiating between high and low flow oxygen systems.
Oxygen delivery devices 1.
Oxygen loss is negligible but with these devices high concentrations of oxygen are not available.
Flow rate 1 4l min 4l will dry the nose 2l is more comfortable.
Rightward shift facilitates unloading of o2 a 40 air entrainment 10l min o2 flow will produce a total gas flow of approximately 40l min 28 air entrainment 4 l min o2 flow will produce a total gas flow of approximately 44 l min.
Documented hypoxemia in adults children and infants older than 28 days arterial oxygen tension pao2 of 60 mmhg or arterial oxygen saturation sao2 of 90 in subjects breathing room air or with pao2 and or sao2 below desirable range for specific clinical situation in neonates pao2 50.